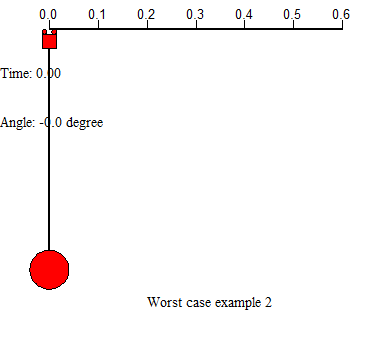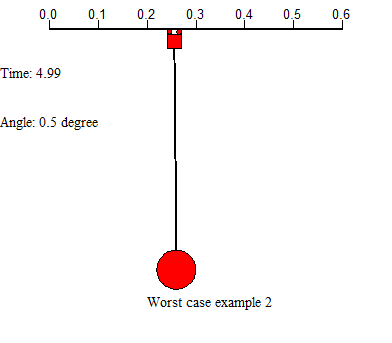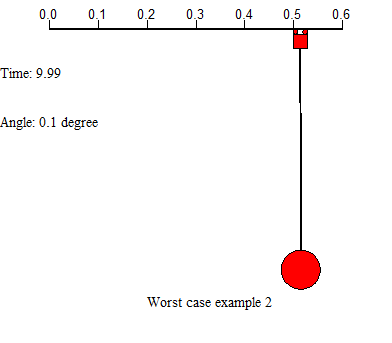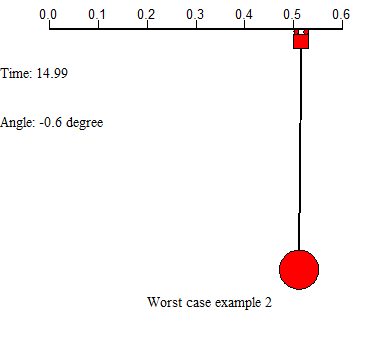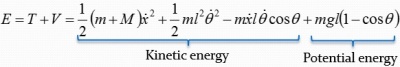Difference between revisions of "Projects:2014s2-80 Swinging Crane Project"
(→Feedback/closed-loop control) |
(→Feedback/closed-loop control) |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
=== Feedback/closed-loop control === | === Feedback/closed-loop control === | ||
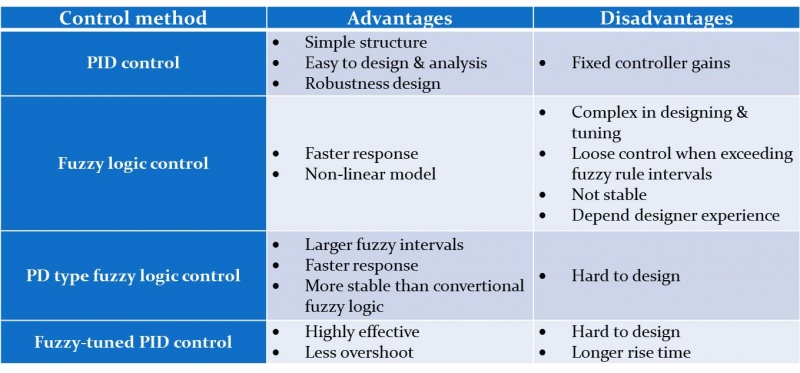
[[File:Table of control methods comparison.jpg|800px|thumb|left|Table 1.Control methods comparison]] | [[File:Table of control methods comparison.jpg|800px|thumb|left|Table 1.Control methods comparison]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
== Previous work == | == Previous work == | ||
Revision as of 23:28, 28 May 2015
Project aim: Swinging Crane project is aim to transporting a payload from one place to another and reducing the consuming time as much as possible. Using the software of Simulink and ControlDesk on computer to create and simulate a system model. Through the hardware of dSPACE board, amplifier and simulator to realise practical control, which is move the trolley for 0.5 meters and count the consuming time from starting movement to fully settled. The outcomes are supposed to realize multiple control methods, which includes automatic and manual control. The system performance should be improved compared with last year results. This project also could be used for helping high school student to understand the principle of control systems.
Contents
Project introduction
Technical background
Gantry cranes are wildly used in industry, for lifting heavy objects by a hoist which is fitted in a hoist trolley and can move horizontally on a rail or pair of rails fitted under a beam.
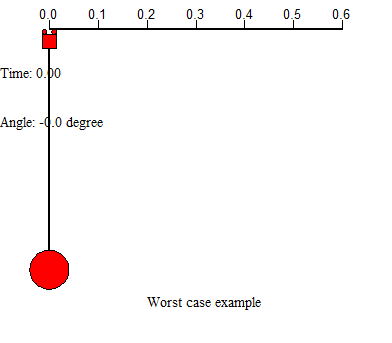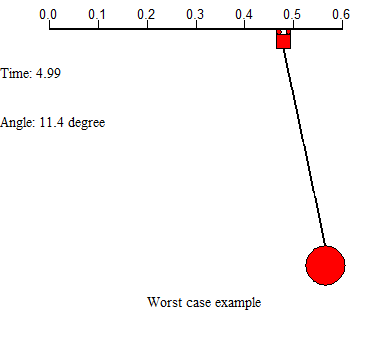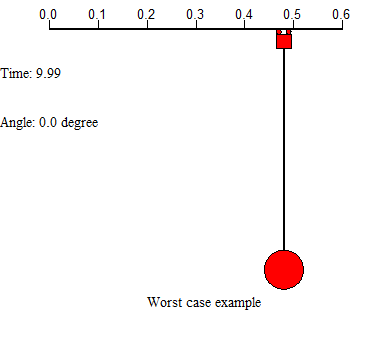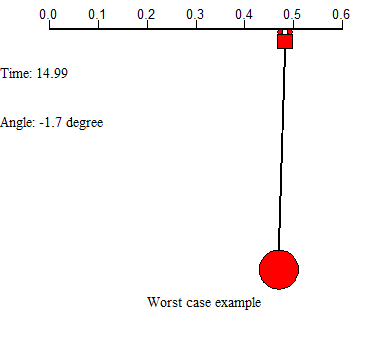
There are two examples on the above shows 2 worst case in controlling the system. First example uses a large force applied on the trolley, leads the residual swinging angle at the end is very large and the system cost much time to settle. Second example uses small force to drive the trolley from start, but the trolley movement is too slow, which costs a lot of time either. In this project, we will concentrate on designing appropriate feed forward input to the system, and add controllers to help control the system motion, further improve the system performance.
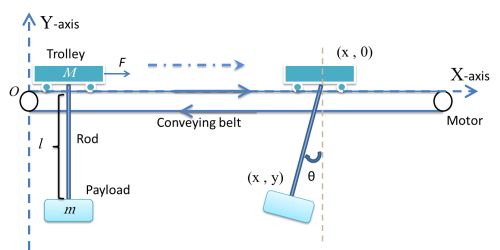
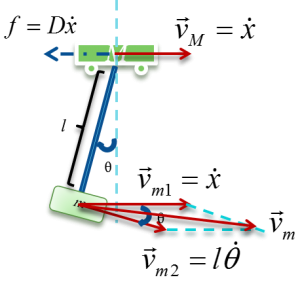
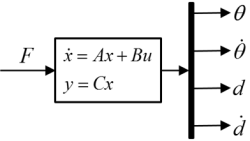
Figure 1 demonstrates the model of swinging crane, the DC motor controls the trolley to horizontally move a load in a short distance. There are two encoders to record the data, one is the moving distance, and another is sway angle of the load. By giving a signal from operation control system, it will generate a DC current from a current source, then injecting it into a motor, which would drive the conveyor belt. There is a trolley placed on one side of the belt, and start moving towards another side. At the bottom of the trolley, using a rod stand for the hoist, connect with a load. At the start of transporting the loads, it will cause accelerated, corresponds to a traction force, effect on the trolley. There occur an angle between the rod and vertical. After the trolley stops, the loads may turn to oscillate. If the initial angle large, the oscillation duration roses, which is a potential risk to the people on the ground.
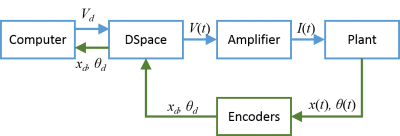
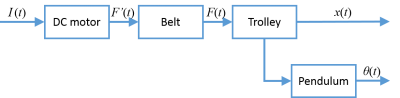
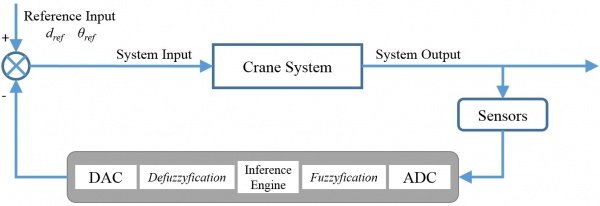
The system is operated inside a flow, shown as Figure 2. Input signal is generated from Simulink, goes into the plant through dSPACE and amplifier. The outputs of the plant are measured by two encoders, and send back to dSPACE, finally transfer to the computer. The dSPACE and amplifier components will introduce later. The plant is the real model of the system, the transfer relationship is shown in Figure 3. The current flows into DC motor, which drives the belt on the grid. The trolley is bind on the belt, thus it has the same acceleration with the belt. There are two outputs from the, the trolley position and the swinging angle of the pendulum.
Motivation
The gantry crane system could be identified into separate sections: linear motion and swinging pendulum. The goal is to minimum the time used to transport loads and reduce the swinging oscillation as minimize as possible. The pendulum was studied by Galileo, Huygens, Newton, Hooke and all the leading figures of 17th-century science. Since the long history on the study, pendulum theory has been almost perfect, but still exist imperfection in applied to practical. In this project, the basic model is simple gravity pendulum. To analyse the motion parameters of pendulum, Newton’s classical mechanics Laws are applied. In traditional education, Newton’s lows are taught in high-school physics lecture. The theorem is abstract to student, and divorced from the practical application. The gantry crane system is a representative application, and easy to understand, thus it is suitable for demonstration teaching purpose.
Objectives
The aim of swinging crane project is to demonstrate research component of project, examine and improve last year’s project, perform analysis, show understanding of theoretical principles, simulations and experiments, then improve system robustness, calculating instantaneous energy and optimize system motion trajectories. The 5 objectives of this project are shown as bellow:
1.Modelling of system – physical principles, approximates which can be used to simplify model (e.g. linearized model).
2.Selection of reference trajectories-trade-offs, constraints, optimization.
3.Calculation and control of “energy” stored in pendulum-means for damping energy.
4.Simulation of system- investigates and checks performance.
5.Experimental demonstration- interfacing operation, model verification.
Background
Crane system
The crane system model can be dismantled into 2 parts: a pendulum subsystem with fixed trolley position and a free trolley position while there is no pendulum oscillation drive by a DC motor. The system control methods including feed forward control and feedback control.
Feed forward/open-loop control
Feed forward control can change the system output directly through a pre-defined path. Feed forward control is usually used with feedback control since a feedback control system is required to track set point changes and to suppress unmeasured disturbances in system response. In system theory, reference input is necessary to control the plant, and how to set an appropriate input signal is difficult. Moreover, there exists a lot of methods for optimal input-shaping, which is aim to improve system performance through system input, instead of controller. This usually has more obvious effect than the feedback control.
Feedback/closed-loop control
Previous work
The swinging crane real system is designed by the workshop of University of Adelaide. Some analysis has been done by previous group, a simple PID control and current manual control have also been developed. Thus some data of the model could use by directly looking up their reports.
Figure 4 gantry crane system is studied by last year project group. This model is based on lumped-mass model, which ignore the mass and the elongation of the rod caused by the tension force. Both of the trolley and payload are considered as point mass and moving in two-dimensional x-y plane.
System modelling
Simple pendulum model
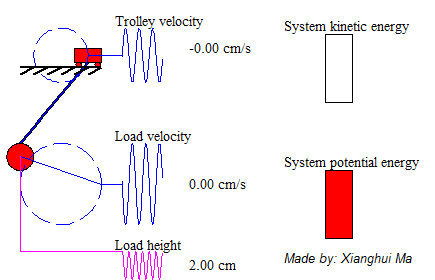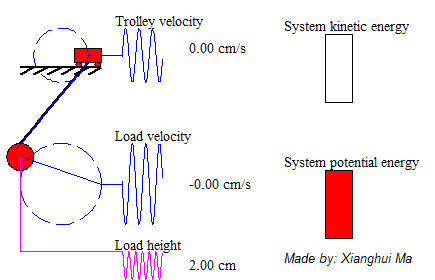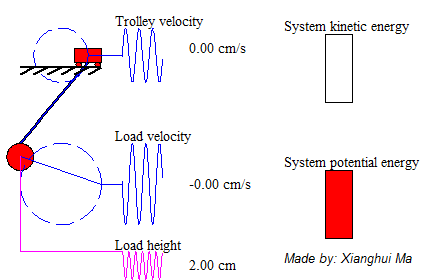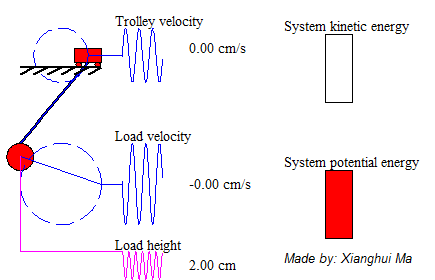
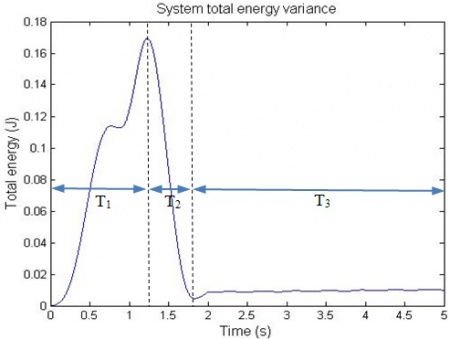
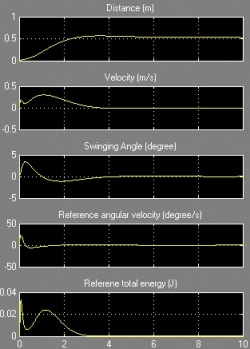
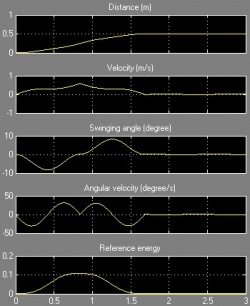
System total energy is the summation of kinetic energy of the trolley, the potential energy and kinetic energy of pendulum load. The animation on the left shows a free-trolley-position movement demonstration without friction or air-drag. It shows the energy conservation law, which means the total energy is constant all over the time, and in this particular case the system kinetic energy is complementary to potential energy. Consider a trail of total energy in a system process, shows as Figure 5, in where T1 is the acceleration time period, T2 is the deceleration period and T3 is the remain oscillation period. The magnitude of system total energy in T3 is a constant value with frictionless assumption. The left animation illustrates the system remaining oscillation relationship in T3.
System equations
According to Figure 6, the system total energy could be expressed as:
Taking the force relation, the system transfer function is
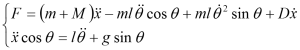 ,
if the pendulum swing a small angle(i.e.less than 10 degrees), the above equations could be reduced to
,
if the pendulum swing a small angle(i.e.less than 10 degrees), the above equations could be reduced to
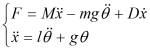 .
.
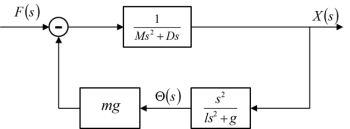
By taking the Laplace transform, the system transfer function is
![]() .
.
The above equations could also write as state-space model form. Assume the state variable ![]() , and state equation
, and state equation ![]() the state matrices are
the state matrices are 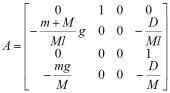 ,
,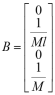 and
and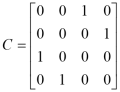 .
.
Control methods designing
PID control
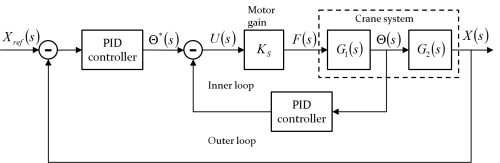
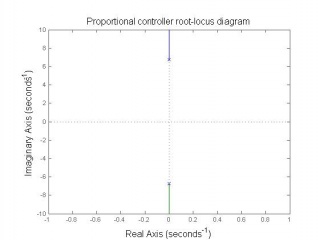
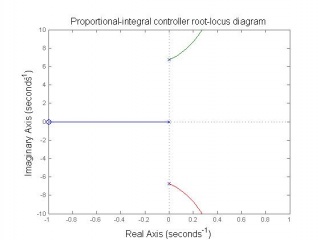
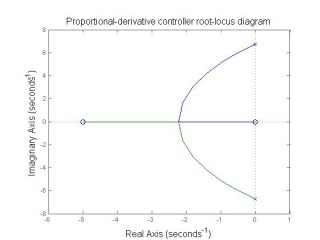
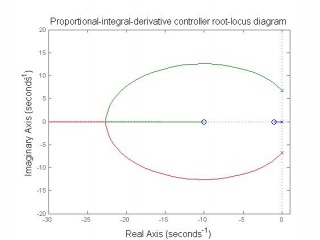
In this project the Figure 7 block structure is used. There are two PID controllers used to control the two state variables feedback. The PID controller parameters are designed by selecting appropriate , and gains through analysing the root-locus diagrams and considering the system robustness.
Inner-loop controller design
Observing from the above root-locus diagrams, PD controller has simple construction and enough to insure the stability of open-loop system.To ensure control system robustness, i.e. system is not sensitive to connector length l and load mass m changing, a robustness designing for inner-loop controller parameters is essential. The inner-loop system robustness with above parameters will have the tolerance of connector length changing 10% (from 0.389m to 0.475m), mass of load changing 44% (0.308kg to 0.792kg).
Outer-loop controller design
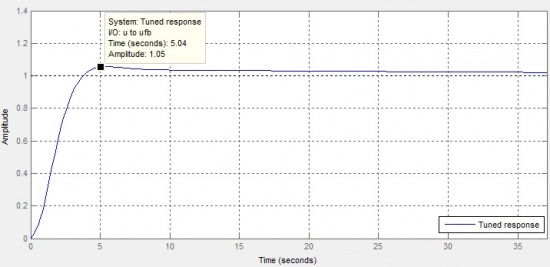
The outer loop is designed using the Simulink built-in function, PID self tuning with considering the following conditions: • Overshoot ≤ 5% • Settling time ≤ 5s • Steady state error ≤ ±1%
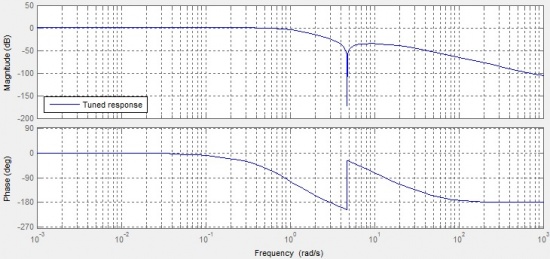
The outer loop PID controller response tuning design is shown as Figure 8. The tuning Bode diagram is shown as Figure 9.
Fuzzy-logic control
Fuzzy logic control is a rule-based control method. The controller is designed with a set of fuzzy rules for both input and output sides. Figure 10 shows the basic structure of a fuzzy control system.
In classic control field, the precision of a control system modelling effects the system behaviour most. The dynamic information of the system state could help achieve the goal of accuracy control. However, the number of the state variables are too much for a complex system, and they may have influence to each other, thus it is difficult to describe the system state correctly. Fuzzy logic control uses the idea and theory of fuzzy algorithms to describe the system state. Fuzzy control is a nonlinear control method, and it also belongs to intelligent control branch. In general, a control engineer will use classic algorithms (of the classic PD type, for example) if the system can be modelled and fuzzy algorithms (of the fuzzy PD type, for example) if the system cannot be modeled (or can only be partly modeled).
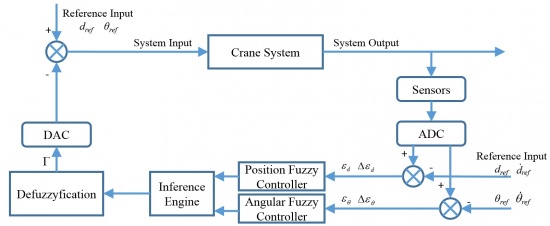
In this project, there are 4 state variables, which defined in previous. Based these variables, two fuzzy controllers are used. The system simulation diagram shows as Figure 11.
Fuzzification design
The fuzzyfication process uses fuzzy state variables to describe the system. Assume the state variables and control variable are:
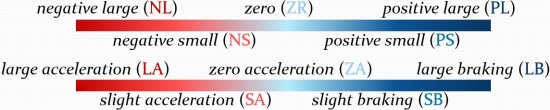
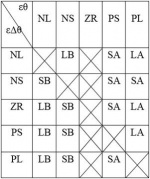
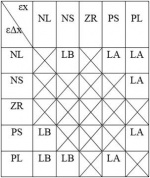
The state variables considered can be positive, zero or negative, also can be large and small. Presume there are 5 quantified intervals set for input variables, in which are “negative large” (NL), “negative small” (NS), “zero” (ZR), “positive small” (PS) and “positive large” (PL). While there are 5 quantified regions set for output, in which are “large acceleration” (LA), “slight acceleration” (SA), “zero acceleration” (ZA), “slight braking” (SB) and “large braking” (LB), illustrates as the fuzzy rules bar.
Fuzzy rules define
The fuzzy rules are defined as term of Θ (ZR, PS; AS) for example. Table 7 presents the corresponding relationship of the angular error, the angular acceleration error and the correction output acceleration. Table 8 is the position rule matrix, similar as Table 7. The example rule could be interpreted with the following implication: If the angular error εθ is ZR and the variation of the angular error is PS, then the trolley acceleration Γ is AS.
Defuzzification design
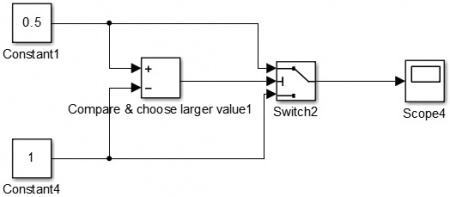
The process of selecting the output from the two fuzzy controllers is called defuzzification. There are several methods to achieve defuzzification: the method of the center of gravity, the method of the maximum, and the method of the mean value of the maxima. In this project, the simplest one, maximum method, is used. In Simulink, this selection is realized through switch function, shown as Figure 12, and the result in scope is 1 in this case.
Position manual control
Hardware test and interfacing
Results comparison
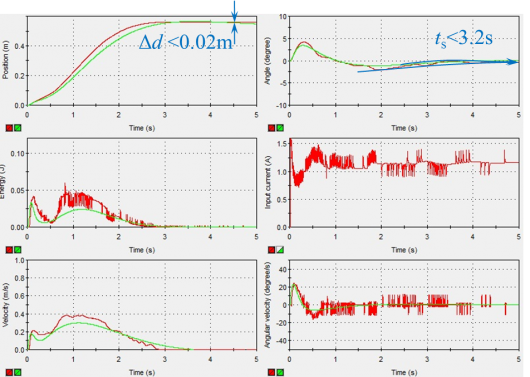
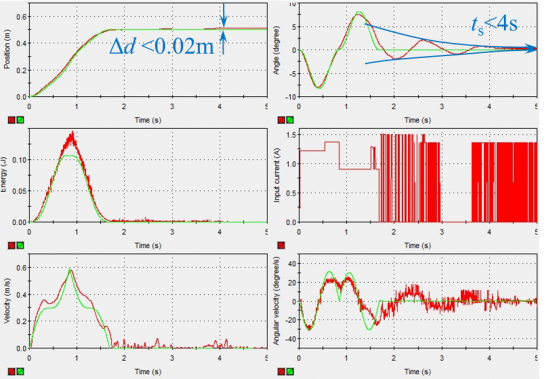
Figure 17 and Figure 18 shows the practical results compared with simulation results of feedback control using PID and fuzzy logic controller. The green line represents for simulation trajectory, while the red line represents the practical data. The system settling time and position error has been labeled out on each figure.
Conclusion
Skills training and professional development
Among the simulation state, the required skills include analysis and modelling physic model, Matlab simulation programming, dSPACE using method, and encoder and sensor devices using knowledge. During the project period, the team cooperation ability, the ability to communicate or negotiate with supervisor, the capability of literature review, time management and project management skill and other professional skills would be developed. All of the skills are essential for further research activities and could be apply to career.
Group members
Liyan Yi
Xianghui Ma
Supervisors
Dr.Wen Soong [1]
Dr Braden Phillips [2]
References
[1] A. Ridout, “Anti-swing control of the overhead crane using linear feedback”, Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Australia 9(1/2), 1989, 17-26.
[2] A. Ridout, “New feedback control system for overhead cranes”, in Proceedings of the Electric Energy Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 1987, vol.1, pp.135-140.
[3] APPLETON MARINE, INC., 2014, “Knuckle boom crane: Model KB”, viewed 29/08/2014,<http://www.appletonmarine.com/marine-products/cranes.html>
[4] B. Cazzolato, “Advanced PID Control (2013) Control System Implementation”, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, Australia. 2013.
[5] B. Kolar & K. Schlacher, 2013, “Nonlinear control of a gantry crane”, in Computer Aided Systems Theory- EUROCAST, 14th International Conference, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, pp.289-296.
[6] C. Yang, “Swinging Crane Simulator”, School of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 2014.
[7] DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development, dSPACE Gmbh. P aderborn, Germany. 2013
[8] E. Abdel-Rahman, A. Nayfeh & Z. Masoud, 2003, “Dynamics and control of cranes: a review”, Journal of Vibration and Control 9, 863-908.
[9] Galieo’s Pendulum: from the rhythm of time to the making of matter, RG.Newton, London, England, 2004.
[10] K. Sultan, “Inverted Pendulum, Analysis, Design and Implementation”, Institute of Industrial Electronic Engineering, PCSIR, Karachi, Pakistan, Rep. 2003.
[11] M. Ahmad, A. Nasir, M. Najib & H. Ishak, “Anti-sway Techniques in Feedback Control Loop of a Gantry Crane System”, Control and Instrumentation Research Group (COINS), Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, University Malaysia Pahang, 2009.
[12] M. Mattews, C. Gauld & A. Stinner, “The Pendulum”, Springer, Vol.13, No.4-5 and Vol.13, No.7-8, the Netherlands, 2005.
[13] M. Solin, W. Di & A. Legowo, “Fuzzy-tuned PID Anti-swing Control of Automatic Gantry Crane”, Department of Machatronics Engineering, International Islamic University Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 7, January, 2008.
[14] M. Zawawi, J. Bidin, M. Tumari & M. Saealal, “Investigation of Classical and Fuzzy Controller Robustness for Gantry Crane System incorporating Payload”, in Third International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Modelling & Simulation, Pekan, Malaysia, 2011.
[15] S. Bruins, “Comparison of Different Control Algorithms for a Gantry Crane System”, HAN University, Arnhem and Nijmegen, The Netherlands, Intelligent Control and Automation, January, 2010, pp.68-81.
[16] W. Du, Z. Xie, F. Lu & Y. Cao, “Gantry crane dynamic modelling and motion control”, Applied Mechanics and Materials, Vol.419, 2013, pp.649-653.
[17] W. Soong, “DC Machines: Parameter Measurement and Performance Prediction”, School of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 2008.
[18] X. Bai, “Swinging Crane Simulator”, School of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 2014.
[19] X. Yu & W. Yao, “Optimal Composite Nonlinear Feedback Control for a Gantry Crane System”, Department of Automation, Xiamen University, Hefei, China, 2012, pp.601-606.
[20] A. Benhidjeb & G. Gissinger, “Fuzzy Control of An Overhead Crane Performance Comparison with Classic Control”, Control Eng. Practice, Vol.3, No.12, 1995, pp.1687-1696.
[21] dSPACE_guide_encoder
[22] M. Solihin & Wahyudi, “Sensorless anti-swing control strategy for automatic gantry crane system: soft sensor approach”, International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems, ICIAS IEEE, 2007, pp.992-996.
[23] K. Astrom & T. Hagglund, “PID controllers: Theory, Design and Tuning”, 2nd ed, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709, USA: ISA – The Instrumentation, Systems and Automation Society, 1995.
[24] M. Solin & Wahyudi, “Fuzzy-tuned PID Control Design for Automatic Gantry Crane”, International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems, ICIAS IEEE, 2007, pp.1092-1097.