Difference between revisions of "Projects:2020s1-2430 The Ball Bearing Motor Mystery"
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[File:Figure 1 The electromagnetic effect theory.png|thumb|center]] | [[File:Figure 1 The electromagnetic effect theory.png|thumb|center]] | ||
| − | + | [[File:Gruenberg.png|thumb|center]] | |
'''Thermal expansion''' | '''Thermal expansion''' | ||
Revision as of 20:03, 18 October 2020
Contents
Project team
Honours students
- Fengyuan Zhan
- Liam Martin
Supervisors
General project description
The ball bearing motor is a mystery because to this day no engineer knows how it works! No one understands the physical principle at all. Doing some experiments is necessary to investigate this motor and why it is that it rotates. Understanding the principle is important. It may not be useful for large motors, but it may be interesting for micromotors and micropumps that have numerous applications.
Abstract
The Huber effect was first discoverd at 1959. The effect acts on the ball bearing motor that the motor can continuously rotate in either direction when supplied with either a DC or AC supply. This effect has attracted numerous academics to resesarch the base principle to support the action of Huber effect. This experiment is aim to verify the availability of some of these theories by searching the relationship among torque and angular velocity of the motor as well as the other relative elements. An simple simulation experiment was made by COMSOL to investigate the simulated phenomenon of Huber effect without damaging the ball bearing motor. Meanwhile an encoding wheel and a photosensor are adopted to investigate the relationship of torque and angular velocity of the motor. The completion of the project is expected to help the future investigation of the application of ball bearing motor in micro-electromechanical systems(MEMS) technology and driving further investigation for the Huber Effect into the correct way simultaneously.
Aim
This project is aim to find out more useful imformation of the ball bearing motor and investigate the avaibility of the supported therories behind the motor with practical experiments. It is expected to use COMSOL to perform a simulation ball bearing motor experiment to assist the investigation of practical experment.
Background
The principles of the motor are still a mystery in academia. There are still many disputes on how the motor works. Three main theories are the most popular and all of Them will be shown below.
Theories
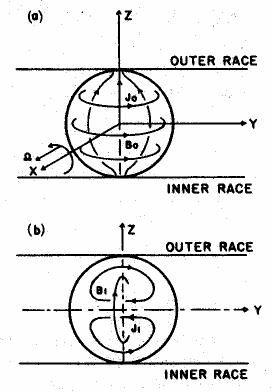
Electromagnetic effect
The theory 'Electromagnetic effect’is raised by Gruenberg in 1977.[1] It states that each single ball has primary volume current density J0 and primary magnetic field B0 when connecting current sources. When the ball is moving caused by shaft spinning, a new current density J1 and related magnetic field B1 will be produced in the new position. The interaction between J0 and B1 as well as interaction between J1 and B0 will force the ball to move to further position then drive the shaft spinning, and produce further current density and magnetic field then create a new force. This cycle is responsible for the continuous rotation of the shaft.
Based on the analysis of the electromagnetic effect theory, the motor torque is proportional to the angular velocity and the squared value of the supply current.
Thermal expansion
The theory 'Thermal expansion' is purposed by Marinov, indicated that “the ball bearing motor is not an electromagnetic motor but a thermal engine.”[2] When the current go through the whole circuit in ball bearing, the contact points between balls and races will have high temperature due to the high resistances. It leads to the expansion of contact points, and further changes the shape of balls into a slightly ellipse but not staying in a circle. With an initial torque, the ellipse will rotate to a new position and new contact points will be expanded to complete the next movement cycles.
The another experiments has been done by Watson, William and Crimp, they got a further conclusion that the torque-current under the situation of invarious speed should be linear.[3]
Plasma discharge
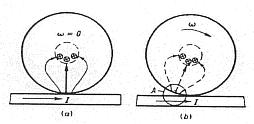
The theory of 'plasma discharge’firstly proposed by Polivanov, Netushil and Tatarinova in 1973. They ascribed the Huber effect to the plasma discharge . Sparking which is the result of Lenz’s Law will occur at the points between the last contact point of bearing balls and the race when the motor is spinning. A force is produced as a result of the interaction of induced currents within the magnetic field disturb the symmetry of the current and flux distribution established by previous contact points. And this interaction will be repeated to sustain the force leading to rotating.[2]
As a result of investigation, they summarized the rotating force is proportional to the squared value of currents.
Method
Motor size
The motor built for these experiments is believed to be the smallest version ever built. A ball bearing motor typically has a shaft diameter size of 10mm whereas this ball bearing motor has a shaft diameter of 1mm. The reason for scaling down the motor design is to scale down the destructive currents experienced in the bearings which may help prolong their service life. A housing was made for this motor to ensure it had good alignment. Two metals screws were drilled into the housing and would make contact with the bearings. These screws acted as the terminals for the bearings and would provide the current to the bearings.
Measuring equipment
An Arduino mega board along with code downloaded from the internet specifically written for measuring angular speed and torque was used to measure this motors characteristics.
To measure the angular speed of this motor, an encoder and photo interrupter are used. An encoder is simply a disc mounted on the motor shaft with some sections of it cut out or drilled out, so that light may pass through that section and the rest of the encoder will not pass light through. When the encoder is turning, it will periodically obstruct the photo interrupter. The photo interrupter will sense when it is being obstructed and send a signal to the Arduino board. The Arduino board uses this combination of the obstructed signals over a period of time to calculate angular speed.
To measure the torque, a prony brake and load cell are used. A prony brake is simply a clamp and arm. The clamp is mounted to the shaft tightly but not too tight as the shaft needs to be able to turn while the clamp and arm are stationary. The load cell is a steel bar and strain gauge which can detect forces applied to it. When the motor is turning, the prony brake will want to move from the friction of the motor shaft. The load cell is placed under the arm of the prony brake which apply a downwards force due to the friction from the turning shaft. The load cell signal is then amplified and sent to the Arduino board and calculates the torque. A potential problem with this method is that the ball bearing motor is known to only produce little torque and this setup may stall such a small motor, in which case the prony brake should be taken off and only angular speed is measured.
Experiments
This motor was to be tested in three different environments; normal conditions, submerged in demineralised water, and submerged in nitrogen gas. The purpose of submerging the motor in demineralised water and nitrogen gas is that they will suppress arcing in the bearings and act as a heat sink for the motor which will help prolong its life. The reason the water needed to be demineralised is because normal water conducts electricity whereas demineralised does not.
Liquid metal motor
Another experiment has been designed the eliminates the bearings from the design and instead considers two conductive discs submerged in mercury in their place. Power is supplied to the discs through the mercury. If this motor works, it will allow for prolonged testing and may additionally disprove the thermal expansion theory. It should be noted that bearings are still used in this design but only the secure the motor in place.
Power supply
A power supply 30V 20A power supply was used for this experiment. The ball bearing motor typically runs on a much larger current but due to its reduced size, this power supply was an appropriate choice.
Results
Simulation
A simpler version that two discs connected by a shaft has been built. However it fail to collect useful imformation to support the practical experiment. The reason could be the groups fail to build a model that absolutely consistent with the actual situation with the COMSOL software being a complex software that requires a lot of training and experience in order to master and use it effectively.
Practical
This motor was operated from a range 0.5A to 3A, unfortunately however this motor failed to sustain rotation on its own for these currents. Without a current applied, the motor shaft had good rotation but as soon as the power supply was connected and turned on, the motor became more difficult to turn. When the power supply was disconnected the shaft rotation would become better again.
It was speculated that the reason for poor rotation was heating and expanding in the bearings making them difficult to turn. Therefore, the motor was tested in demineralised water which would help cool the bearings. However, the motor still failed to turn and would become more difficult to turn when the power supply was connected.
Due to the failed results from the motor in air and demineralised water, the nitrogen experiment was cancelled as it is highly expected it will yield similar results.
The motor was only increased to a max of 3 amps of current because at which point the bearing would get hot and deform shape rendering it useless.
The mercury motor experiment has not been commenced at the time of writing this and hence no results or conclusions can be made. This is due to delays and difficulties brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic delaying the project and staff with expertise on handling and using mercury not being available.
Conclusion and discussion
There are several theories as to why this small motor failed to operate.
First is the ball bearings bulging and making the bearings ineffective. It is known the motor does not produce much torque and it may not be able to overcome the bearings bulging too much. This theory seems the most likely due to retarded rotation the motor experiences when a power supply is connected
Secondly is the quality control of the bearings. These bearings were bought online through eBay due to them being substantially cheaper than ball bearings of the same size from local bearing suppliers. However, it was noticed that these bearings were not identical to each other and some of them had a slightly larger inner diameter than others. Some bearings also were better at turning than others. For the experiments, bearings were compared to make sure similar sized and good turning bearings were chosen for the experiment but it is possible that due to poor quality, these bearings do not work. This may also be related to the first theory.
Thirdly is motor misalignment. A housing that the motor would sit in tightly and be secured down was built for the purpose of making sure the motor is aligned, however it is possible that the motor is still not perfectly aligned due to subtle bends in the fragile shaft and unequal balances on the encoder that are not noticed.
Finally, whatever sustains rotation for this motor may not work when it is made this small. As the motor is still a mystery, it is hard to say if it could work when it is this small.
Due to this motor failing to sustain rotation, it is a possible indication that this motor may is not be a good choice for a micromotor.
References
[1] H. Gruenberg et al, "The ball bearing as a motor," Am. J. Physics, 46, pp. 1213-1219, 1973.
[2] Joo L. Choo, Wen L. Soong and D. Abbott,“Toward Characterization of Huber’s Ball-Bearing Motor”,Smart Structures, Devices, and Systems II, edited by Said F. Al-Sarawi, Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 5649 (SPIE, Bellingham, WA, 2005), [Online]. Available: http://proceedings.spiedigitallibrary.org/. .
[3] Y. Shen, B. K. Tay, B. Thompson, W. L. Soong, B. R. Davis, D. Abbott, “Investigation of the Huber effect and its application to micromotors”, Part of the SPIE Conference on Electronics and Structures for MEMS Royal Pines Resort, Queensland, Australia • October 1999, [Online]. Available: http://spiedigitallibrary.org/.