Project Team
Donald Dong Zhang
Dennis David Kimtai
Supervisors
Professor Christophe Fumeaux
Dr Shengjian (Jammy) Chen
Introduction
Natural Rubber, Buffalo Leather and Blue Foam are used as substrates for the realization of wearable antennas integrated into clothing.
Background and Motivation
The reliability of wearable communication systems can benefit from high performance antennas integrated into clothing. Emerging wearable communications systems will increasingly require flexible antennas which can be integrated into clothing and are able to adapt their shape to various movement of the body. This will allow exploiting the area of clothing to create efficient antennas in critical applications such as communications and tracking for defence or safety personnel, or monitoring of patients in a hospital.
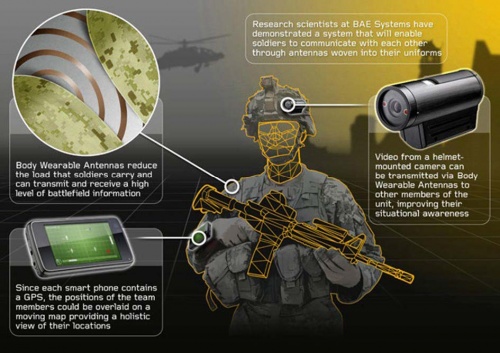
Fig 1. Wearable antennas in defence
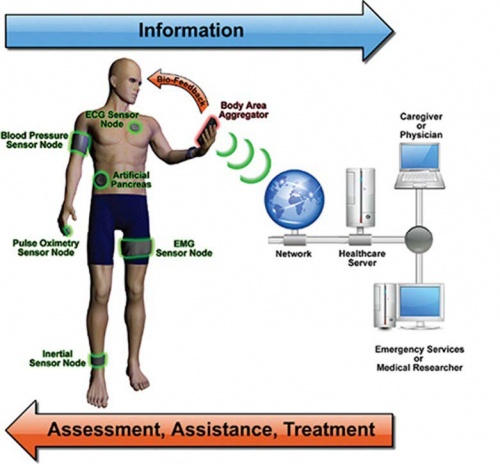
Fig 2. Wearable antennas in health care
Aims and Objectives
This project considers the use of widely available flexible materials as substrates for the realization of wearable antennas. The project focuses on material characterization and related design aspects. It involves antenna theory and computer-assisted design with state of the art electromagnetic simulations tools.
Material Characterization
The substrates materials should be lightweight, small size, flexible and robust to achieve good communication characteristics without much variation in performance.
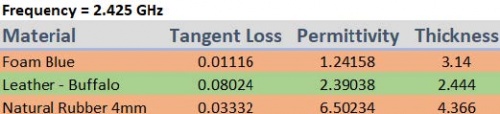
Fig 3. Materials properties
Design Aspect
In this project antenna theory and computer simulation software (CST) was used to evaluate the use of different materials for two different types of wearable antennas:
- Monopole Antenna
- Planar Inverted-F Antenna (PIFA)
Monopole Antenna
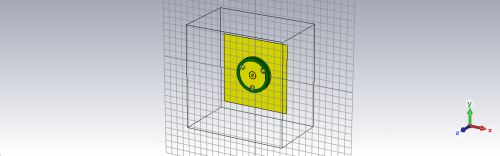
Fig 4. Monopole Antenna using Leather substrate
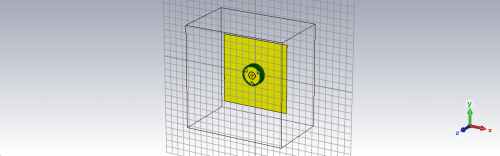
Fig 5. Monopole Antenna using Rubber substrate
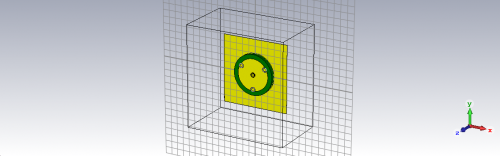
Fig 6. Monopole Antenna using Foam substrate
Planar Inverted-F Antenna (PIFA)

Fig 7. PIFA Antenna using Leather substrate
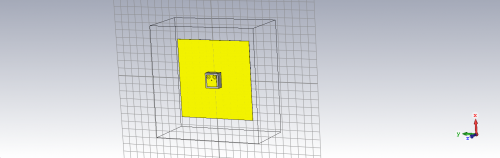
Fig 8. PIFA Antenna using Rubber substrate
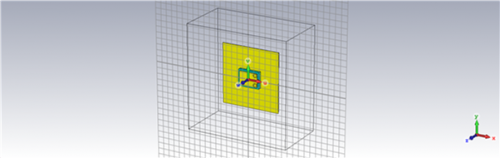
Fig 9. PIFA Antenna using Foam substrate
Simulation Results
Reflection Coefficient
Monopole
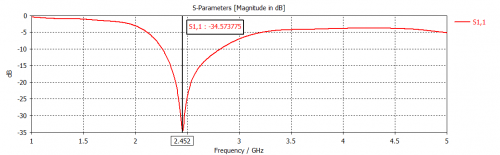
Fig 10. Reflection coefficient for Monopole Antenna (Leather Substrate)
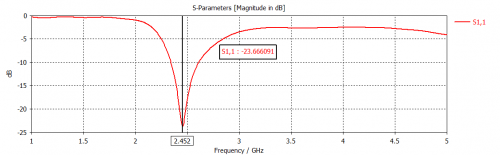
Fig 11. Reflection coefficient for Monopole Antenna (Rubber Substrate)
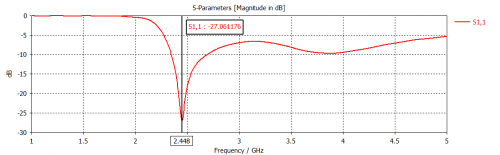
Fig 12. Reflection coefficient for Monopole Antenna (Foam Substrate)
PIFA
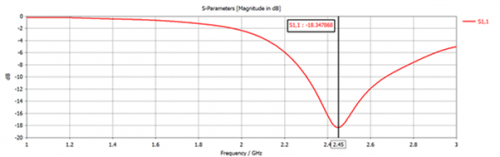
Fig 13. Reflection coefficient for PIFA Antenna (Leather Substrate)
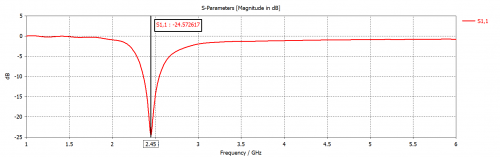
Fig 14. Reflection coefficient for PIFA Antenna (Rubber Substrate)
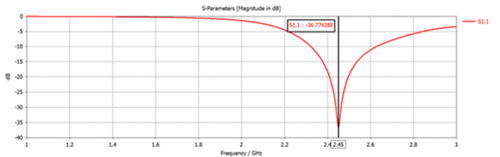
Fig 15. Reflection coefficient for PIFA Antenna (Foam Substrate)
Directivity and Efficiency
Monopole

Fig 16. Directivity and Efficiency for Monopole Antenna (Leather Substrate)
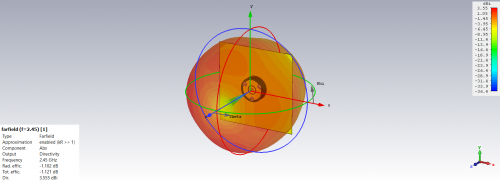
Fig 17. Directivity and Efficiency for Monopole Antenna (Rubber Substrate)
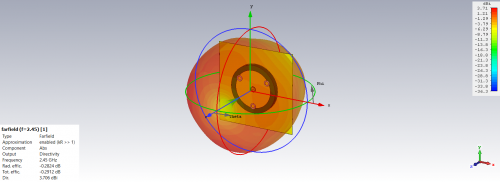
Fig 18. Directivity and Efficiency for Monopole Antenna (Foam Substrate)
PIFA
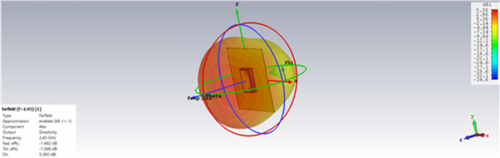
Fig 19. Directivity and Efficiency for PIFA Antenna (Leather Substrate)
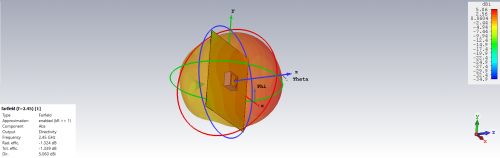
Fig 20. Directivity and Efficiency for PIFA Antenna (Rubber Substrate)
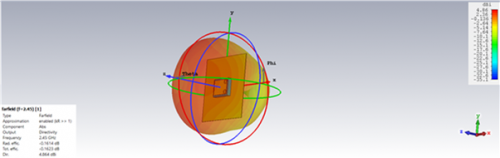
Fig 21. Directivity and Efficiency for PIFA Antenna (Foam Substrate)
E field distribution
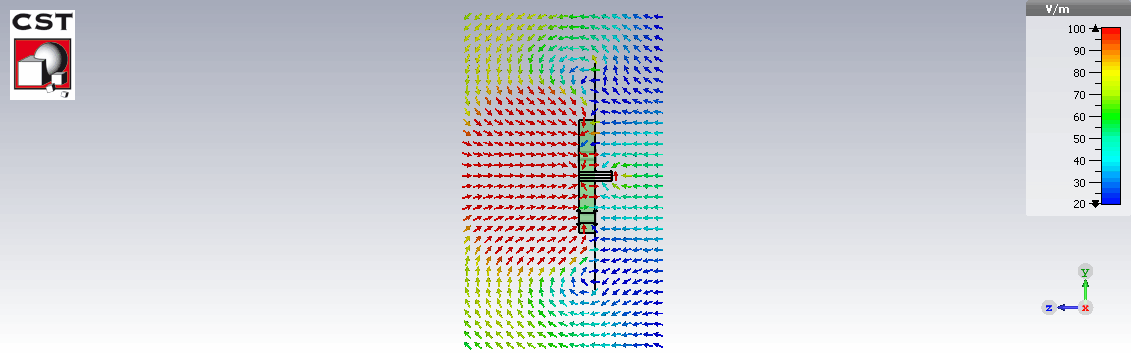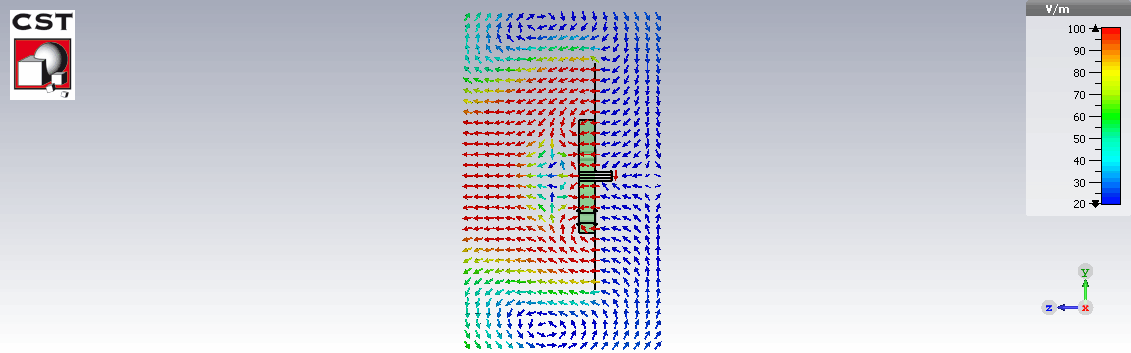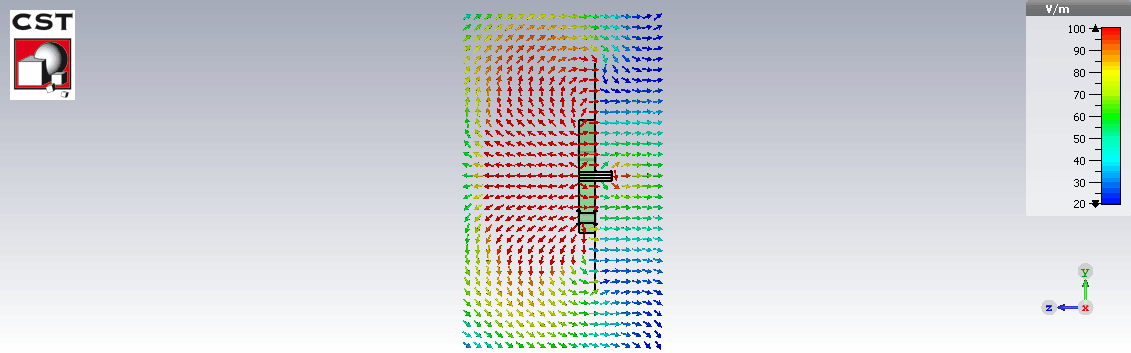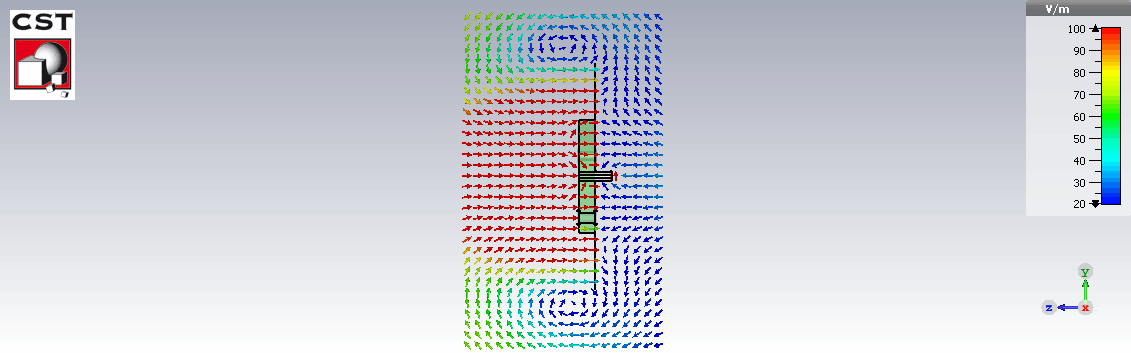
Fabrication
Monopole Antenna
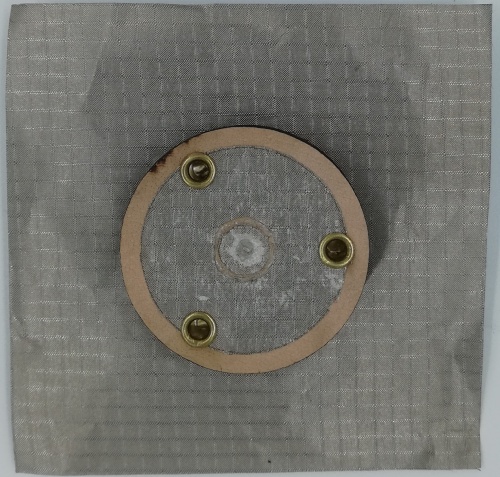
Fig 22. Monopole Antenna fabricated using Leather Substrate (Front View)
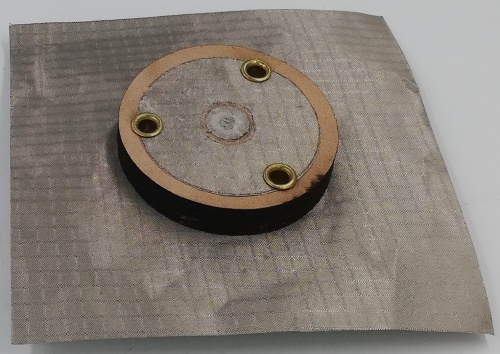
Fig 24. Monopole Antenna fabricated using Leather Substrate (Side View)
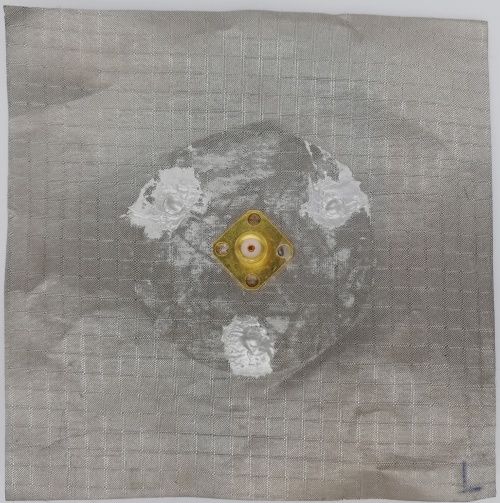
Fig 23. Monopole Antenna fabricated using Leather Substrate (Back View)
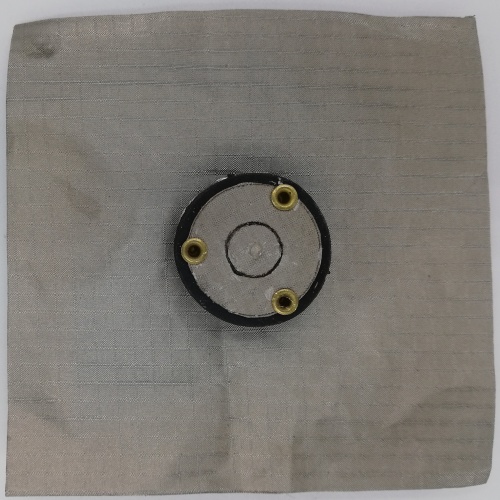
Fig 25. Monopole Antenna fabricated using Rubber Substrate (Front View)

Fig 27. Monopole Antenna fabricated using Rubber Substrate (Side View)
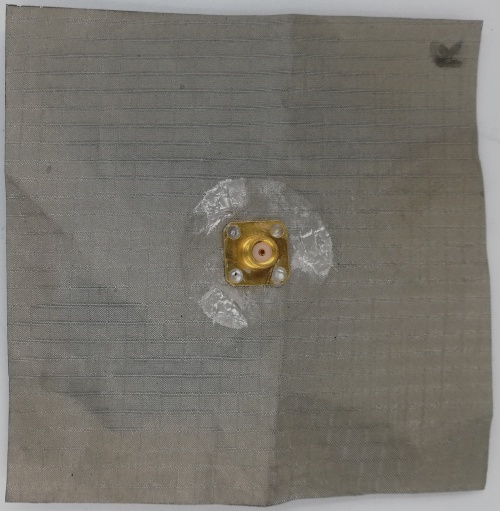
Fig 26. Monopole Antenna fabricated using Rubber Substrate (Back View)
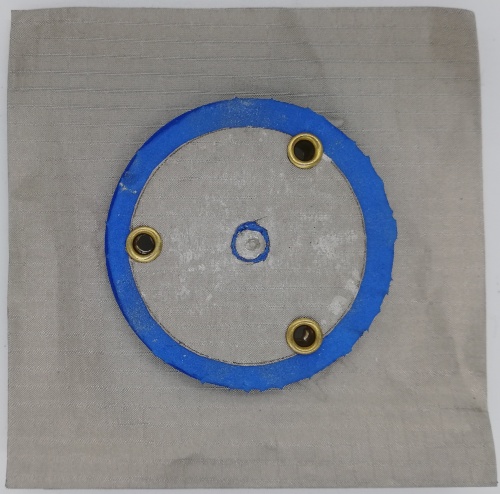
Fig 28. Monopole Antenna fabricated using Foam Substrate (Front View)
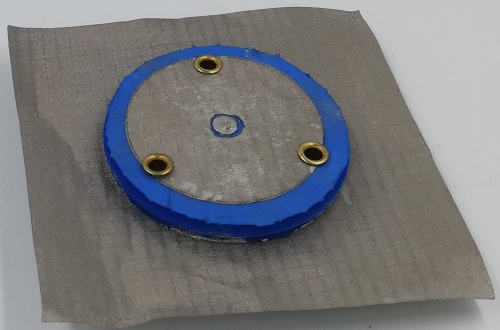
Fig 30. Monopole Antenna fabricated using Foam Substrate (Side View)
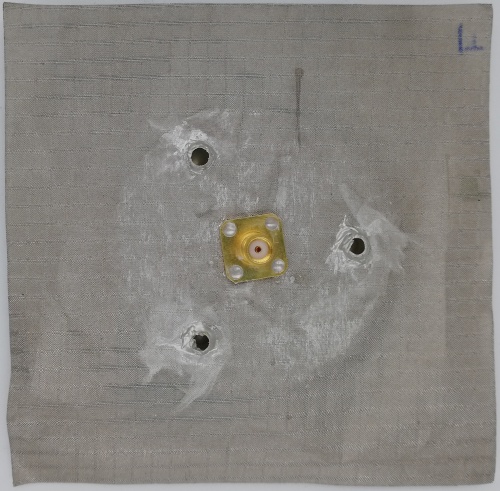

Fig 29. Monopole Antenna fabricated using Foam Substrate (Back View)
PIFA
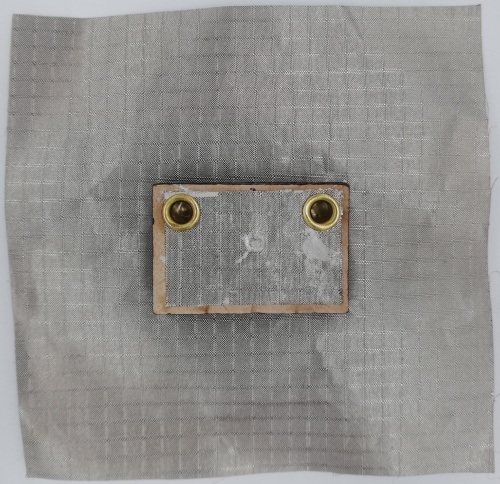
Fig 29. PIFA Antenna fabricated using Leather Substrate (Front View)
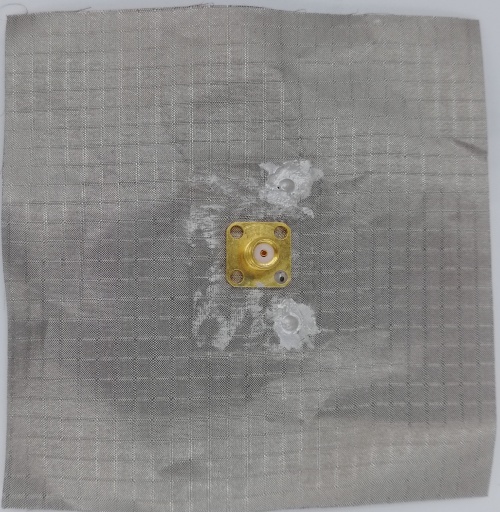

Fig 30. PIFA Antenna fabricated using Leather Substrate (Back View)
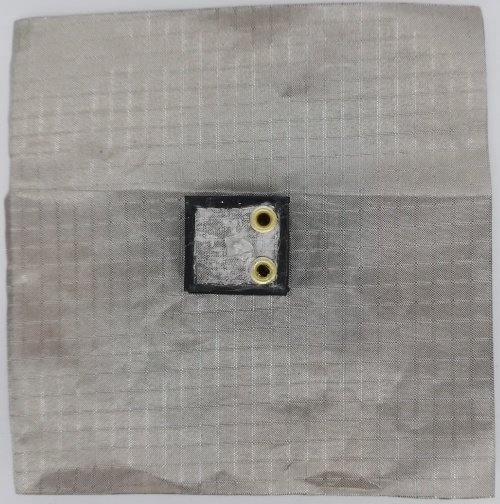
Fig 31. PIFA Antenna fabricated using Rubber Substrate (Front View)
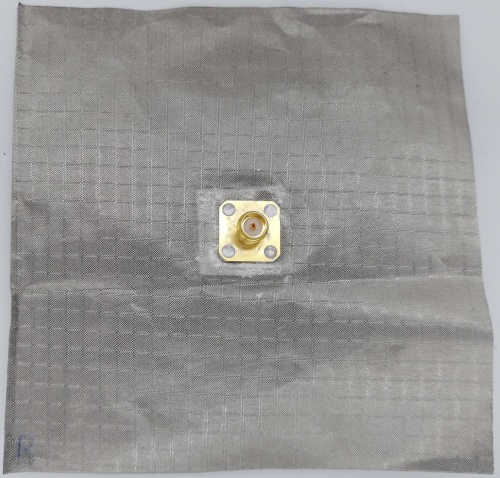
Fig 32. PIFA Antenna fabricated using Rubber Substrate (Back View)
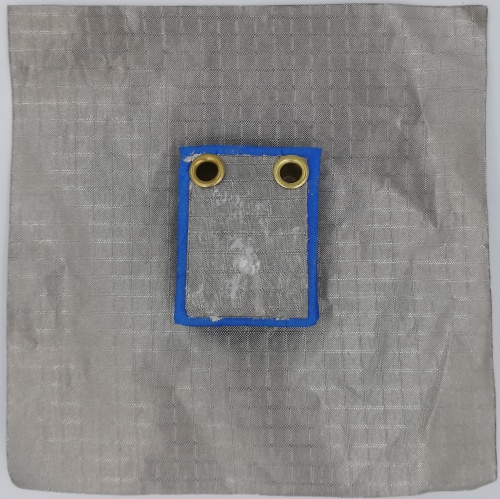
Fig 33. PIFA Antenna fabricated using Foam Substrate (Front View)
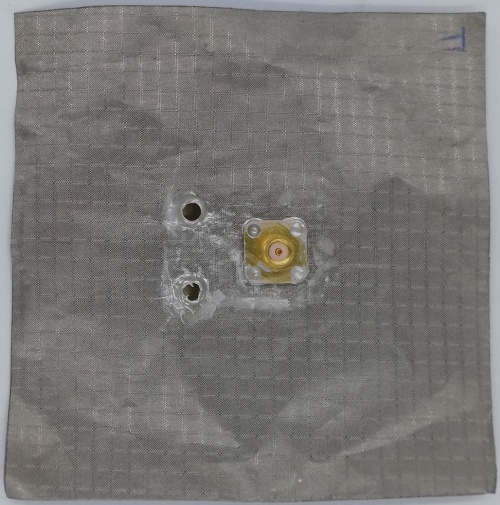
Fig 34. PIFA Antenna fabricated using Foam Substrate (Back View)
Achievements
Fabrication results are expected to match the results from simulation.




































