Projects:2014S1-35 Human Activity Recognition to Support Independent Living
This project aims to build a Hybrid RFID sensor tag which could renovate the way of tag-to-reader communications based on the Wireless Identification and Sensing Platform (WISP) 4.1 DL version developed by Intel Research Seattle.
Contents
Project information
The holistic goal of the Human Activity Recognition to Support Independent Living project is to determine if the use of privacy preserving radio-frequency identification technology and wireless sensor technology to detect patient activities can form the basis for a technological solution to support independent living, specifically, build a hybrid-semi-passive sensor tag which could renovate the way of tag-to-reader communications based on the Wireless Identification and Sensing Platform (WISP) 4.1 DL version.
A WISP is generally a sensing and computing device that is powered and read by a standard off-the-shelf RFID reader [1].
Currently, there are three common approaches to provide power and tag-to-reader communications. The first one is the passive sensor tag, it receives all its operating power from an RFID reader. It is battery-free but with short wireless communication distance and the requirement of proximity to RFID reader is high [2]. The second one is the semi-passive sensor tag, it uses batteries to run the chip’s circuitry, but communicates by drawing power from the reader. The last one is the active sensor tag, it provides long wireless communication distance but in the expense of high cost and low lifetime since it requires one-time batteries to power for the tag and radio.
Project Aims
An enhanced version of the sensor tag is proposed.
The individual aim of this project is to formulate, design and build a Battery Management Unit (BMU) capable of charging/discharging under different circumstances. The BMU shall be smart to decide when to use the battery to power the WISP and be charged by the UHF reader.
It is supposed to combine all the advantages from the current three types of sensor tags and achieve better overall performance with low power consumption. Longer communication distance and better life time shall be realized.
Outline of proposed work
- Battery Test
- Building Hybrid RFID Sensor Tags
Project Approach
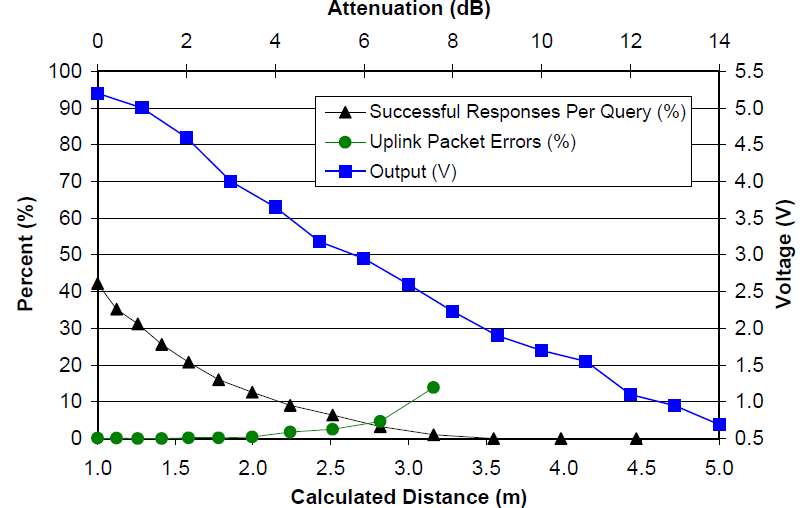
Original WISP performance
- The WISP communication and error rates as a function of RF attenuation and calculate distance.
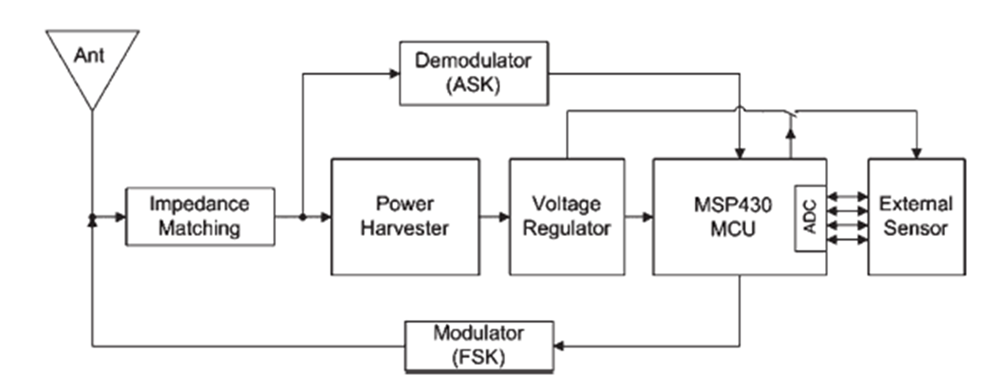
Block Diagram
- Origianl WISP
The original WISP design block diagram with no battery.
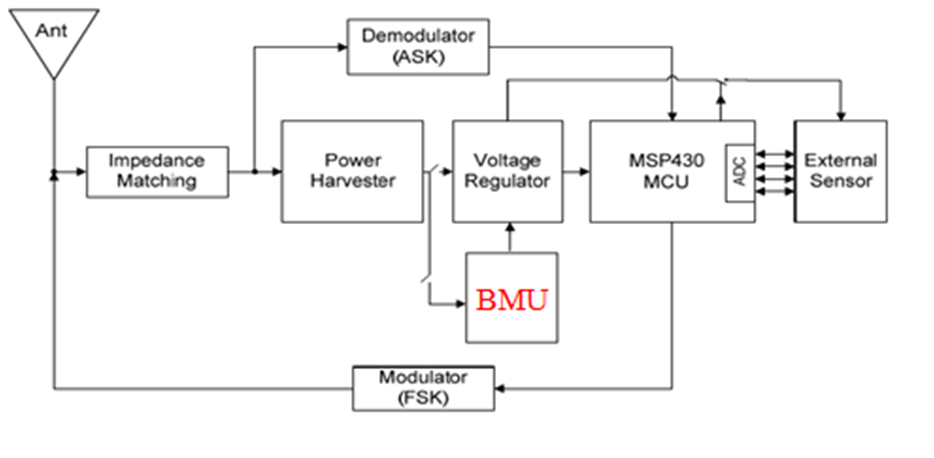
- Proposed Design
Our proposed design with Battery Management Unit (BMU). The external battery would be charged and discharged under different distance between the RFID reader and the WISP corresponding to the output voltage.
Team
Group members
- Mr Yuchen Dong
- Mr Han Xue
Supervisors
- Dr Said Al-Sarawi
- Dr Damith Ranasinghe
Resources
- USB Key Debugger
- RFID Reader, Antenna
- Standard PC
References
- [1] Intel Research Seattle, “WISP Wiki,” [Online] https://wisp.wikispaces.com (Accessed: 2 October 2014).
- [2] A. P. Sample et al., “Design of an RFID-Based Battery-Free Programmable Sensing Platform,” IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., vol. 57, no. 11, pp. 2608 2615, Nov. 2008.