Projects:2014S1-12 Exploring RF Energy Harvesting for Wearable Sensors
Contents
Project information
Introduction
Wearable electronic devices are in growing number of uses. Recent years, a number of wearable low power sensors are used in the area of health-care [1] such as electrocardiogram (ECG) and electroencephalography (EEG). These sensors are low energy required which means that several μW [2] is sufficient enough to drive these kinds of sensors. Some devices require longer lifetime working under some circumstances [2], so having a renewable energy source instead of using battery source becomes necessary.
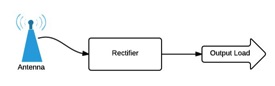
In this project, the rectenna is designed in two parts which is shown on Figure 1. The first part is a dual band antenna which is able to collect ambient RF energy with frequency of GSM 900 and GSM 1800. The second part is a rectifier which is used to convert RF energy to DC energy in order to make the rectenna be able to provide DC power. A schematic of the design concept is illustrated below.
Design Target
- Design and manufacture a dual-band patch antenna that is able to collect the ambient RF energy with the frequencies of GSM900 and GSM1800.
- Design and manufacture a wide-band dipole antenna that is able to collect the ambient RF energy with the frequencies of GSM900 and GSM1800.
- Design and manufacture a rectifier which is able to convert the RF energy of GMS900 and GMS1800 into DC energy.
Design Approach
- Understand the basic approach to design antennas and the circuit of rectifiers.
- To design antennas
- HFSS is used during the design process
- Draw a parametric model in HFSS
- Obtain simulated results
- Analyse simulated results and hence optimise the design
- Test the limitation of the dimension accuracy in manufacturing and human body effects in HFSS
- Manufacture the antenna and test the performance
- To design the circuit of the rectifier
- ADS is used uring the design process
- Design the system in top level.
- Design the circuit to obtain the value of each component.
- Optimize the schematic-based design in ADS
- Layout the schematic design
- Process EM simulation
- Use ADS to do EM Optimisation
- Manufacture the circuit and test its performance
Team
Group members
- Mr Mingzhe Li
- Mr Hung-Kai Mai
- Mr Hanqing Wang
Supervisors
- Dr Thomas Kaufmann
- Prof Christophe Fumeaux
Resources
- Bench 22 and 23 in Projects Lab
- Voltage Control Oscillator
- DC generator
- Network Analyser
- Anechoic Chamber
- Spectrum Analyser
- Software
- ANSYS HFSS
- Advanced Design System (ADS)
References
[1] Giuseppina Monti, Laura Corchia Giuseppina Monti and Luciano Tarricone, “UHF wearable rectenna on textile material," IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, vol. 61, no. 7, July. 2013
[2] Benton H. Calhoun, Naveen Verma, David D. Wentzlo_, Seong-Hwan Cho, “Design Consideration for Ultra-Low Energy Wireless Microsensor Nodes" IEEE TRANSACTION ON COMPUTERS, vol. 54, no.6, June. 2005