Projects:2014S1-36 What are Social Appliances? Building your Tomorrow Today…
This project is proposed to build a "Social Fridge".
Project Information
Project Aim
We plan to build a "Social Fridge" which can assist people to manage their usages of food stored in the fridge. To achieve this, we are to use the RFID reader and barcode scanners associated with cameras to identify the items, and use the weighing sensors to measure the weight of those identified items. Furthermore, temperature sensors are used to get the local temperature and humidity. Finally, all the measured and recorded information is then pushed to a Facebook page for users to read and share with their friends. In addition, all relevant information will also be displayed on a touch screen which is placed on the door of the fridge.
Working Scenario
When the fridge door is opened, the angle measuring sensormeasures the opening angle of the doorand at the same time, it also triggers on the barcode scanners and RFID reader. When the user put items into or take items from the fridge, a beep reminding sound is played when the item is scanned, and cameras and weighing sensors are triggered on to get photo and weight of the item. The changes of the total weight of items on the shelves decide whether items are taken out or putted in, if the total weightincreases, then items are put in, if the total weight decreases, then items are taken out, and the difference between the current total weight and the previous total weight is the weight of the current item. As for the temperature and humidity data in the fridge, they are collected by T&H sensors which are working all the time. After the processing is done in raspberry pi, the analyzed data is then displayed on the display panel (a touch screen)and published on a Facebookpage (in this project, we use the fan page of Auto-ID Lab University of Adelaide). https://www.facebook.com/adelaideautoidlab
For items in the freezer, the working procedure is the same as described above. And for items stored on the shelves on the fridge door, the collection of the identification information (RFID tag code, barcode, photos) and the weight of the current item is done on the on-door scanning panel.
Components analysis
To implement functionalities described in the scenario, we use the following hardware and also program for them.
Hardware
- Fridge:Mitsubishi 325L 2-door Bottom Mount Stainless Steel Fridge
All the hardware will be integrated in this fridge.
- Raspberry Pi:Mode B
Monitor and control all the software modules and give in-time response.
- Barcode Reader:XL-200 Omni-directional Barcode Scanner Module
- RFID suit: M6E-DEVKIT
In this project, both barcode reader and RFID reader are used to identity items in the fridge.
- Camera:ELP-USB500W02M-45A
The camera is used for recording items when putted into the fridge.
- AngleSensor:534-500:500R OHM 10 TURN PRECISION POT
This is used for recording at what stage the drawer in the freezer is pulled out.
- Temperature&Humidity Sensor: DHT22
Record the temperature and humidity in the fridge.
- Touch Screen:14" glossy open-frame LCD, 1366x768 px, 256K (18-bits) colors, viewing angles: (L/R:45, U/L:15-35)
Present the information recorded and serve to control something in the future.
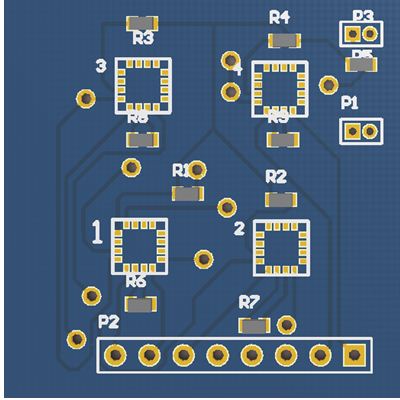
- PCB designed for Strain-gauge
Software
After finishing data collecting and analysing, the social fridge posts status on facebook fan page of AutoID Lab of Adelaide[1].
Information will also be presented in the screen which is fixed on the door of fridge. A interface makes it organised.
Integration Plan
Items to be integrated in the fridge
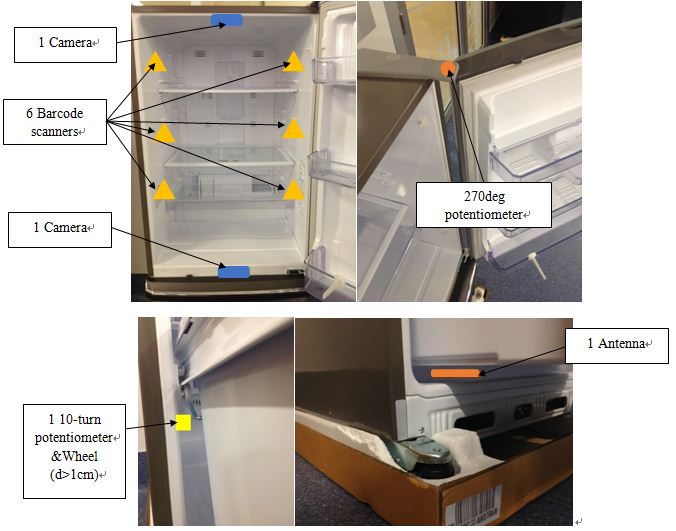
a) A 270deg potentiometer for the fridge door
b) A 10 turn potentiometer for the freezer drawer
c) A rubber wheel for the 10 turn potentiometer (with diameter >1cm)
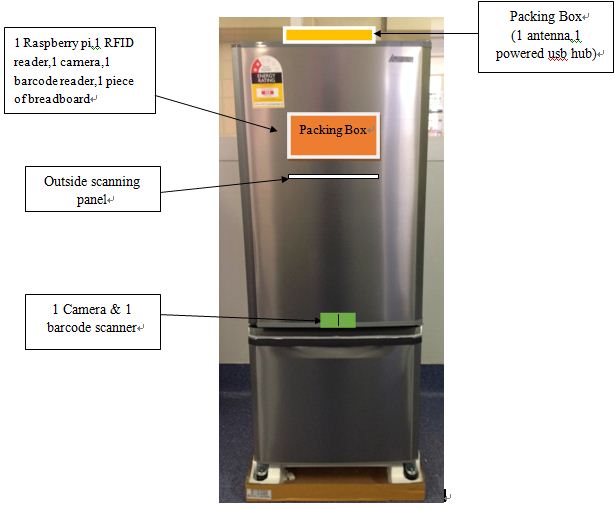
d) A packaging box (for one camera, one barcode reader, RPi, RFID reader, PCBs and speaker) on the door of the fridge
e) A scanning shelf under the packing box on the door of the fridge
f) 8 barcode reader (2 for each shelf * 3, 1 for the freezer, 1 for the outside scanning shelf)
g) 4 cameras (1 on the top of fridge, 1 on the bottom of fridge, 1 on the outside scanning shelf, 1 for the freezer)
h) 3 T&H sensors (2 in the fridge & 1 in the freezer)
i) 1 weighing panel on the outside shelf (on the scanning shelf outside)
j) A packing box on the top of the fridge (for Powered USB hub and one antenna)
k) 1 touch screen on the packing box
l) 5 weighing sensor modules (3 for fridge, 1 for freezer and 1 for outside shelf)
m) 1 antenna on the top of the fridge, 1 antenna on the bottom of the fridge
n) 1 RFID signal blocking panel (between the fridge and the freezer)
o) Power supplies (for RPi, RFID and Touch screen)
Integration position
Note: all the bodies of the cameras and barcode scanners will be placed into the sides of the fridge and just let lens out. The touch screen will be taped in front of the on-door packaging box.
Wire & cable connection
i. From top packaging box to on-door packaging box:
a. 1 USB cable (powered USB hub to Raspberry pi)
b. 1 coaxial cable (antenna to RFID reader)
ii. From freezer to on-door packaging box:
a. 1 coaxial cable (antenna to RFID reader)
iii. wires (10-turn potentiometer to breadboard)
iv. wires (DHT-22 wires to breadboard)
v. From on-door packaging box to top packaging box:
a. 1 USB cable (1 camera to powered USB hub)
b. 1 USB cable (1 barcode scanner to powered USB hub)
vi. From fridge to top packaging box:
a. 10 USB cables (7 barcode scanners and 3 cameras to powered USB hub)
vii. From fridge to on-door packaging box:
viii. wires (PCB output wires to breadboard)
ix. wires (2*3 DHT-22 wires to breadboard)
Note: Ideally, all the wires and cables are hidden inside the fridge. Another option is using packaging frame to tape the wires and cables on the outside of the fridge.
Team Management
Team Members
- Mr Chundi Li
- Mr Wenshuo Ma
Supervisors
- Dr Said Al-Sarawi
- Dr Damith Ranasinghe
Acknowledgements
- Mr Ian Linke
- Mr Danny Di Giacomo
- Mr Aubrey Slater
- Mr Pavel Simcik
Resources
- Lab Computer
- Oscilloscope
- Workshop Bench
- Lab Bench
- DC Power Supply
References
[1] S. Luo, H. Xia, Y. Gao, J. S. Jin, and R. Athauda, “Smart Fridges with Multimedia Capability for Better Nutrition and Health”, International Symposium on Ubiquitous Multimedia Computing, pp. 39-44, Oct. 2008.
[2] N. Balta-Ozkan, R. Davidson, M. Bicket, L.Whitmarsh, “Social barriers to the adoption of smart homes”, Energy Policy , vol. 63, pp. 363-374, Dec. 2013.