Projects:2017s1-191 Power Electronics for Inductive Power Transfer (IPT)
Contents
Project Title- Pacemaker Wireless Charging System
Project team
Garth Fernandez
Tuo Jiang
Delana Seneviratne
Supervisor- Dr Andrew Allison
Advisor- Dr Said Al-Sarawi
Abstract
Conventional pacemaker technology currently relies on non-rechargeable batteries to power a cardiac pacemaker. This technology has resulted in patient deaths due to the invasive surgery component of replacing the non-rechargeable battery when battery capacity diminishes. The project explores the benefits of a wireless charging system to power a rechargeable battery inside the body. These benefits include longevity and a reduced need for repetitive surgery. The pacemaker will be treated as a black box. The system needs to provide desirable voltage and current characteristics to charge the battery efficiently, such that the patient doesn’t have to wear the transmitter coil for extended lengths. The wireless charging system consists of a set of transmitter and receiver coils, electronics and a rechargeable battery. The transmitter coil will sit on the skin near the left shoulder while a smaller receiver will be implanted at a distance of up to 1cm in the skin.
Background
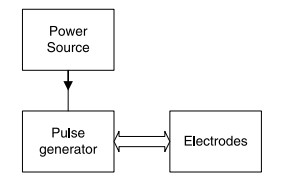
Pacemaker consists of three main modules which are power source, pulse generator and electrodes. Pacemakers monitors heart activity through the electrode leads connected to the heart. The electrodes send a signal to the pulse generator to excite an electrical pulse to control abnormal heart rhythms.
Aim
Develop wireless charging system for pacemaker
Utilize a simple circuit model for a pacemaker to build WPT charging system.
System Design
The system includes three modules, which are transmitter module(with coil), receiver module(with coil) and battery charging module.
Performance
The system can provide around 400mA to the rechargeable battery.
Challenges
The feedback and the battery capacity are two main challenges for the project.